Providing a superior customer experience and having a band of happy customers has not only become a crucial barometer of a company’s success. It’s also a major differentiating factor for consumers choosing who to spend their hard-earned money with.
Customer happiness is typically captured with customer satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) measures. But research from Harvard Business Review shows that these ”fail to tell companies what customers really think and feel, and can even mask serious problems.”
One of the reasons for this is if we look at the concept of happiness in business terms, it’s measured largely on emotion. But emotions exist subconsciously and passively. So asking a customer to rate their satisfaction at a certain point in time barely scratches the surface behind how and why they feel like that.
Take for example a customer’s poor satisfaction rating for a product because they dislike elements of the advertising campaign. Or the influencer the company is collaborating with. The satisfaction score may have very little to do with the actual product itself. But the survey wouldn’t account for this or other external factors that could potentially impact their happiness.
If the customers’ happiness analysis took account of their behaviour and patterns, the real reason behind their poor satisfaction rating would be clear. This approach combines the quantitative aspect of emotion with the qualitative perspective of social sciences, specifically sociology.
Can we really rely on the accuracy of results from standard satisfaction surveys like these? And if not what’s the alternative?
Step 1. Track real-time customer behaviour
Consider the benefits of measuring your live customer data to identify their satisfaction levels. Receiving information based on your customers’ real-time behaviour and patterns, rather than their emotional responses to a written survey, can give you highly relevant insights and a deeper understanding of what your customers truly want.
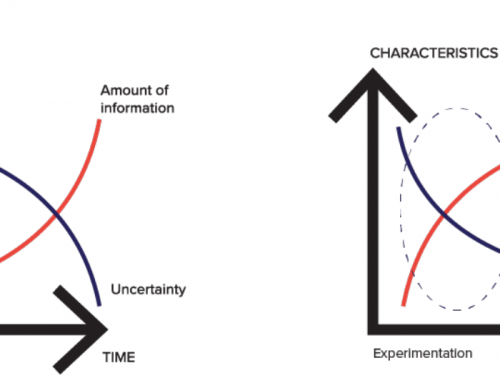
This is the premise of dynamic experimentation which eschews the traditional focus of testing fewer options in the hope of finding the ‘one-size-fits-all’ solution. Why place limitations on the experiment from the outset?
Far better to present all options upfront and track customers’ behavior as it happens. Your customer happiness becomes evident from the rise and fall of interest. Allowing your business to rapidly adjust to real-time data analytics rather than use unreliable surveys based on people’s emotions at a certain point in time.

Step 2. Introduce novelty
It appears we’re all in the pursuit of happiness both in our personal lives and keeping our customers happy. But is too much happiness a good thing?
Don’t we need to feel different emotions in order to grow, learn and experience new opportunities that a perpetual state of happiness might miss?
By introducing novelty, we can create excitement and engage people far more. This increases customer happiness by instilling a strong sense of understanding and empathy. As humans, we’re programmed to be more inquisitive about using something shiny and new. Until we get used to it, and the novelty wears off.
This means you have to find the right level of novelty to keep people happy.
Step 3. Use low-code automation
Dynamic experimentation brings a new dimension to your understanding of how people engage and respond to things in real-time. The power to automate recommender systems and engagement digital technologies means you can learn at pace with people’s behavioural patterns. As people engage further with an experiment, recommenders use their feedback as input into the next contextual recommender. Meaning you can set layers of context and automate your engagement by just understanding a handful of initial behaviors in the community you serve.
Happiness is essential for a company to thrive and succeed. Applying a computational social science approach with machine learning application can catapult your company to the forefront of customer service, relations and sales.
Click here to learn more about dynamic experimentation and how ecosystem.ai’s platform can help you detect customer satisfaction in real-time.